Page 467 - Manual de Urgencias de Pediatría 12 de octubre
P. 467
Manual 401-878 29/11/10 17:51 Página 448
448 A.J. Pérez Díaz, P. Rojo Conejo
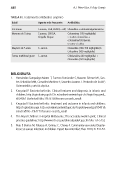
TABLA III. Tratamiento antibiótico empírico
Edad Agente más frecuente Antibiótico
0-3 meses S.aureus, SGB, BGN (E. coli) Cloxacilina + cefotaxima/gentamicina
Menores de 5 años S.aureus, SBHGA, Cefuroxima (150 mg/kg/día)
Kingella kingae > 2 años: cloxacilina +
cefotaxima/ceftriaxona
o como >5 años
Mayores de 5 años S. aureus Cloxacilina (100-150 mg/kg/día) ó
Cefazolina (100 mg/kg/día)
Forma multifocal grave S. aureus Clindamicina (40 mg/kg/día) +
Cloxacilina (150 mg/kg/día)
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
1. Hernández-Sampelayo Matos T, Zarzoso Fernández S, Navarro Gómez ML, San-
tos Sebastián MM, González Martínez F, Saavedra Lozano J. Protocolo de la AEP;
Osteomielitis y artritis séptica.
2. Krogstad P. Bacterial arthritis: Clinical features and diagnosis in infants and
children; http://uptodate.papi.h12o.es/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=pedi_
id/34051 &selectedTitle=1%7E150&source=search_result
3. Krogstad P. Bacterial erthritis: Treatment and outcome in infants and children;
http:// uptodate.papi.h12o.es/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=pedi_id/35431&
selectedTitle=3%7E72&source=search_result
4. The Royal Children´s Hospital Melbourne; Tha accutely swollen joint; Clinical
practice guidelines; http://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/cpg.cfm?doc_id=5152
5. Rojo P, Barrios M, Palacios A, Gómez C, Chaves F. Community-associated Staphy-
lococcus aureus infections in children. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010; 8: 541-54.
448 A.J. Pérez Díaz, P. Rojo Conejo
TABLA III. Tratamiento antibiótico empírico
Edad Agente más frecuente Antibiótico
0-3 meses S.aureus, SGB, BGN (E. coli) Cloxacilina + cefotaxima/gentamicina
Menores de 5 años S.aureus, SBHGA, Cefuroxima (150 mg/kg/día)
Kingella kingae > 2 años: cloxacilina +
cefotaxima/ceftriaxona
o como >5 años
Mayores de 5 años S. aureus Cloxacilina (100-150 mg/kg/día) ó
Cefazolina (100 mg/kg/día)
Forma multifocal grave S. aureus Clindamicina (40 mg/kg/día) +
Cloxacilina (150 mg/kg/día)
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
1. Hernández-Sampelayo Matos T, Zarzoso Fernández S, Navarro Gómez ML, San-
tos Sebastián MM, González Martínez F, Saavedra Lozano J. Protocolo de la AEP;
Osteomielitis y artritis séptica.
2. Krogstad P. Bacterial arthritis: Clinical features and diagnosis in infants and
children; http://uptodate.papi.h12o.es/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=pedi_
id/34051 &selectedTitle=1%7E150&source=search_result
3. Krogstad P. Bacterial erthritis: Treatment and outcome in infants and children;
http:// uptodate.papi.h12o.es/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=pedi_id/35431&
selectedTitle=3%7E72&source=search_result
4. The Royal Children´s Hospital Melbourne; Tha accutely swollen joint; Clinical
practice guidelines; http://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/cpg.cfm?doc_id=5152
5. Rojo P, Barrios M, Palacios A, Gómez C, Chaves F. Community-associated Staphy-
lococcus aureus infections in children. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010; 8: 541-54.